Ask any scientist to list history's greatest discoveries,
and he or she will likely include antibiotics. Antibiotics are medicines made
from certain bacteria, fungi or other organisms that can kill or weaken other
organisms that attack our bodies. Penicillin is the first and most well known
antibiotic. Since its discovery, countless lives have been spared from diseases
that used to be killers.
For a time, antibiotics were thought to cure almost
everything, even cancer. While it would be great, we now know this isn't true.
And we're learning more every day. Like this: A new study says that antibiotics
may not cure most sinus infections.
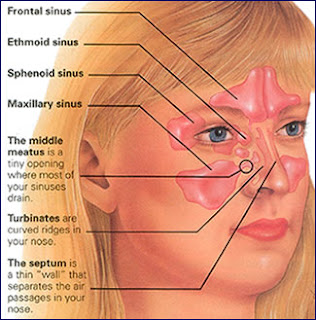
What is sinusitis?
It's often called a "sinus infection," and it
means there's inflammation or swelling in one or more of a person's sinuses.
Sinuses are small spaces in the forehead and cheekbones. They're filled with
air, and their job is to make mucus. When we're healthy, this mucus drains into
our noses. When our sinuses are inflamed, the drainage stops and the misery
starts. Then we have sinusitis – an infection of our sinuses.
Many things can cause sinusitis. That's why one thing may
not be enough to treat it. Allergies, pollen, bacteria, pollution, dust,
viruses – the list of what can irritate our sinuses and set off an infection
goes on and on.
Signs of sinusitis include:
Headaches
Nasal congestion
Runny nose/nasal discharge
Postnasal drip (mucus drips down the throat from the nose)
Sore throat
Fever
Cough
Fatigue
Bad breath
Sinusitis is so common in the United States that 1 of every
5 antibiotic prescriptions written is to treat it. But it looks like those
prescriptions may not be the right answer in many cases.
Bacteria and viruses: two different things
There are two "usual suspects" doctors turn to
first when dealing with an illness. The first group is bacteria. The second is
viruses. Bacteria and viruses aren't the same things. So, bacterial infections
and viral infections aren't the same, either.
Unfortunately, antibiotics don't work on a viral infection.
That's why doctors don't always give us prescriptions for antibiotics:
sometimes we have something viral.
Now, researchers are finding that sinus infections can be
either bacterial or viral.
And lately, more scientists seem to be thinking that viruses
are to blame for most sinus infections.
A new medical study: antibiotics don't work on sinus
infections.
The most conclusive study so far was published in the
February 15, 2012 . It's by the Washington University School of Medicine in St.
Louis and covered 166 adults with sinus infections. Over 10 days, one group of
patients was treated with amoxicillin, a popular antibiotic. The other was
treated with a placebo, which is a "fake" pill sometimes called a
sugar pill. If they needed it, both groups also got over-the-counter remedies
for their symptoms – headache, stuffy nose and sinuses, coughs, fever, etc.
At the end of the 10 days, it was clear that patients taking
amoxicillin didn't feel better sooner, or recover any faster, than those who
were getting the placebo.
Dr. Jane M. Garbutt, the study's lead author, said, "We
hope this study provides scientific evidence that doctors can use with patients
to explain that an antibiotic is not likely to help an acute sinus
infection."
"I think more often than not, these infections are
viral, so antibiotics aren't going to help," Garbutt said. While some
sinus infections may actually come from bacteria, she said, it's hard to tell a
bacterial infection from a viral one. Basically, the only way to know is to
draw a sample from a person's sinus, and that would take surgery.
The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
(CDC) agrees. The CDC's website says viral sinusitis often occurs after a cold
(which is a virus) and usually lasts for less than four weeks. Bacterial
sinusitis can cause symptoms for up to 12 weeks.
No matter which kind you may have, a growing number of
experts think it's best to watch and wait.
Why not take antibiotics just in case?
Besides the fact that taking antibiotics for sinusitis means
spending money on medicine that may not help you, more and more studies say you
could be risking your future health. Why?
It appears that more and more kinds of bacteria aren't being
killed by antibiotics anymore. In medical terms, they're becoming
"resistant" to the drugs.
Each time you take an antibiotic, the bacteria that usually
live in your body are more likely to become resistant to antibiotics. In time,
common antibiotics can't kill infections caused by these resistant germs.
The CDC is very concerned about resistance to antibiotics.
From a public-health point of view, resistance could be a disaster. Overuse of
antibiotics has already led to the rise of drug-resistant infections like MRSA
(Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus). Fighting MRSA is creating a lot
more work at hospitals these days.
So while sinus infections make us feel terrible, if we were
to build resistance to antibiotics by over-using them to treat sinus
infections, what might happen if we're faced with a bacteria-caused epidemic
and no one responds to the drugs?
If you'd like to learn more about this very important issue,
the CDC offers an excellent series of questions and answers about antibiotic
resistance here. It really is something we all need to think about.
Researchers know people aren't going to like this "wait
and see" approach to such a "nasty disease," as Garbutt describes
it. She said: "People have significant symptoms. They feel miserable and
miss time from work. If an antibiotic is not going to be of any benefit, then
what is? That's a question we haven't answered yet. But we are working on
it."
Bottom line?
The CDC says a doctor should never give an antibiotic until
symptoms have gone on for at least seven days. In light of this new research,
your doctor may want to wait even longer before writing a prescription. Even
though it may not be what you want, if your doctor wants to wait, he or she is
doing it for your long-term health. Besides: if your sinusitis is viral, an
antibiotic won't help anyway.
Other options for relief
Some people say they feel less congested when they drink hot
fluids. Others find some relief from warm, wet compresses on their faces. Still
others use warm-water vaporizers. Decongestant nasal sprays can help, though no
one should use them for more than a few days. It's too easy to become dependent
on them.
Several safe and "more-natural" options are out
there, and many people report good results with them. One choice is a saline
(salt) nasal spray. Another is a "neti pot." A neti pot looks like a
little teapot. Its spout is used to gently pour warm saline solution – a mix of
salt and water – into the nostrils. Neti pots, saline sprays, and their
cousins, the more-powerful saline nasal rinses can help flush mucus out of
sinuses. Clearing mucus, especially infected mucus, out of clogged sinuses
brings great relief.
Over-the-counter medicines like ibuprofen can help ease
sinus swelling and the face pain it brings. But doctors say you should also try
to clear your nasal passages, because it will help ease symptoms and clear the
infection.
When to see a doctor, recommends you see a doctor or healthcare provider
if you have:
A temperature of more than 100.4° F.
Symptoms that last more than 10 days.
Multiple episodes of sinusitis in a year.
Symptoms that over-the-counter medicines can't ease.
If your child is younger than three months of age and has a
fever, always call your healthcare provider right away.
Top 5 ways to avoid a sinus infection
Keep your hands clean – regular hand washing is still the
best way to fight disease.
Keep yourself and your family up to date with recommended
immunizations.
Avoid close contact with people who have colds or other
upper respiratory infections.
Avoid smoking or being exposed to second-hand smoke, and
don't expose children to second hand-smoke.
Use a clean humidifier to moisten the air at home.